6 Levels of Autonomy in Self-Driving cars: Explained
Self-driving cars are considered as a future of transport. Millions of dollars are being invested and the sharpest of the minds are being deployed into the research and development of self-driving cars which are also known as autonomous cars. There are debates and discussions happening online about whether self-driving cars are safe on the road or not.
But do we really know the meaning of the term ‘self-driving?
In reality, a Self-driving car doesn’t necessarily mean a car that drives all by itself. The term is very broad. Let’s try to figure out what that means.
For a long time, the automobile industry is trying to include one or the other features which help drivers drive better.
There are functionalities/ systems which provide some assistance and have some level of autonomy correlated to them.
Let’s take an example of the Automatic Lane Correction feature. The car monitors the lane with the help of sensors and tries to bring the car to the center of the lane automatically by using automated steering or automated brakes.
This example also comes into the gamut of self-driving cars. In fact, this scenario comes under the Level 2 of SAE International (Society of Automotive Engineers) autonomy levels for self-driving cars.
So What is meant by SAE levels? Let’s find out.
SAE International is basically a well-known and reputed international organization founded in the year 1905. One of the founders being Henry Ford. Now you get the idea right.
So according to them, there are six levels of autonomy in self-driving cars ranging from zero to five. Zero being the least autonomous and five being completely autonomous.
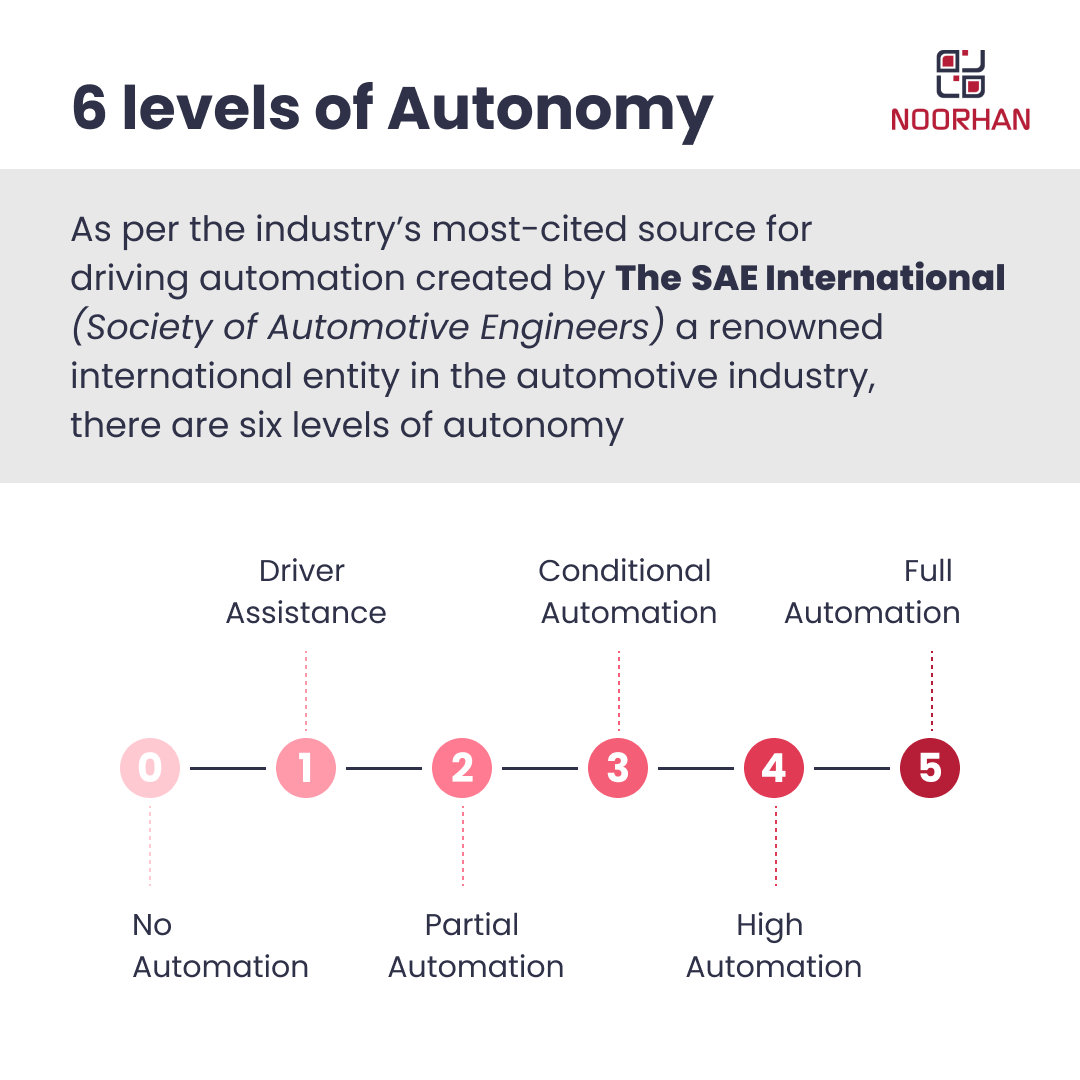
Let's look at each of the levels of autonomy in the self-driving cars
Level 0: No Automation

At this level, the car is all manual & driven 100% by a human. All the tasks related to driving has to be performed by a human
Level 1: Driver Assistance

The car is driven by a human driver.
Some ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) is present to assist certain driving tasks.
Example Features
Automated braking/ Accelerating OR Automated Steering
Level 2: Partial Automation

ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance System) is present to assist some driving tasks simultaneously
The driver must drive the vehicle & monitor the driving environment at all times
Example Features
Braking/ Accelerating AND Steering simultaneously
Level 3: Conditional Automation

The car can perform all the driving tasks in certain conditions.
The ADS (Automated Driving System) can request the driver to take the controls over
Example Features
Level 4: High Automation

The car can perform all the driving tasks in certain conditions.
It’s not required for the driver to monitor the environment,
but the driver has the option to take over the controls
Example Features
Local driverless taxi, pedal/ steering wheel may or may not be installed
Level 5: Full Automation

The car is able to drive itself in all conditions and environments.
No driver is required, all are considered as passengers, but there can be a steering wheel & pedal, just in case the driver wants to take over controls
Example Features
All the normal car functions are controlled by ADS (Automated Driving System).
Wrap Up
We learned that self-driving car is a very broad term. There are different levels of automated systems available in different cars, and based on the type of assistance they provide to the driver or in case they do not require any driver, the level of autonomy varies accordingly.
Images are for representation purposes only.
Recommended read: The ultimate guide to car spare parts